Modern technology is in a state of rapid evolution. Not only are the tools we use becoming steadily more advanced and capable, but the methods of deploying these technologies are also adapting to changing times. If you’re still wondering what the next innovations will be, take a look at these five emerging trends in technology.
Estimated reading time: 6 minutes
The Internet of Things
The term Internet of Things refers to the practice of embedding physical objects with digital tools that increase the utility of that object. Few items can’t make use of such enhancements. Home appliances, lighting fixtures, security systems, and thermostats can all benefit from being linked together and joined to a central control system (such as a smartphone) for ease of use. Even pieces of technology as analog as a generator transfer switch incorporate digital augmentations like QR code readers.
Two concurrent advancements are speeding up the development of this technology trend: Edge computing and 5G connectivity. The fifth-generation technology standard for telecommunications promises greater bandwidth which means faster download speeds. This, in turn, means smoother connections for the large array of devices that make up IoT. Edge computing is less well known and refers to a distributed computing architecture that brings data storage and computation closer to the data source for increased efficiency. Edge computing is a perfect match for devices that generate real-time sensory data, which guarantees that it will be a part of the future of ubiquitous computing.
Human augmentation technologies
One visible consequence of this rapid computerization of society has been the slow melding of humans and machines. Right now, this trend is most commonly seen in the use of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) systems. Virtual reality has been slow to take off, in part because a simulation of reality is rarely as valuable (or enjoyable) as the real thing, especially with computer complexity being a long way from allowing genuinely immersive experiences. Enter augmented reality. AR enhances the user’s real-world experience by adding a layer of computer-generated perceptual data, usually via a wearable device like a pair of glasses. This is incredibly useful in situations where at-a-glance information can mean the difference between life and death, such as on a dangerous worksite or combat zone.
Google Glass made AR famous in 2013, but other companies like Facebook are seeking to expand into the market in the coming years. There will soon come a time when the IoT goes beyond linking things and begins linking people just as reflexively. The next generation of human augmentation will likely see actual cybernetic implants; engineers can already install fingertip magnets to let them sense magnetic fields, and implanted microchip business cards are currently in limited use. Look for the utility of these items to advance as materials science and computer processing power converge.
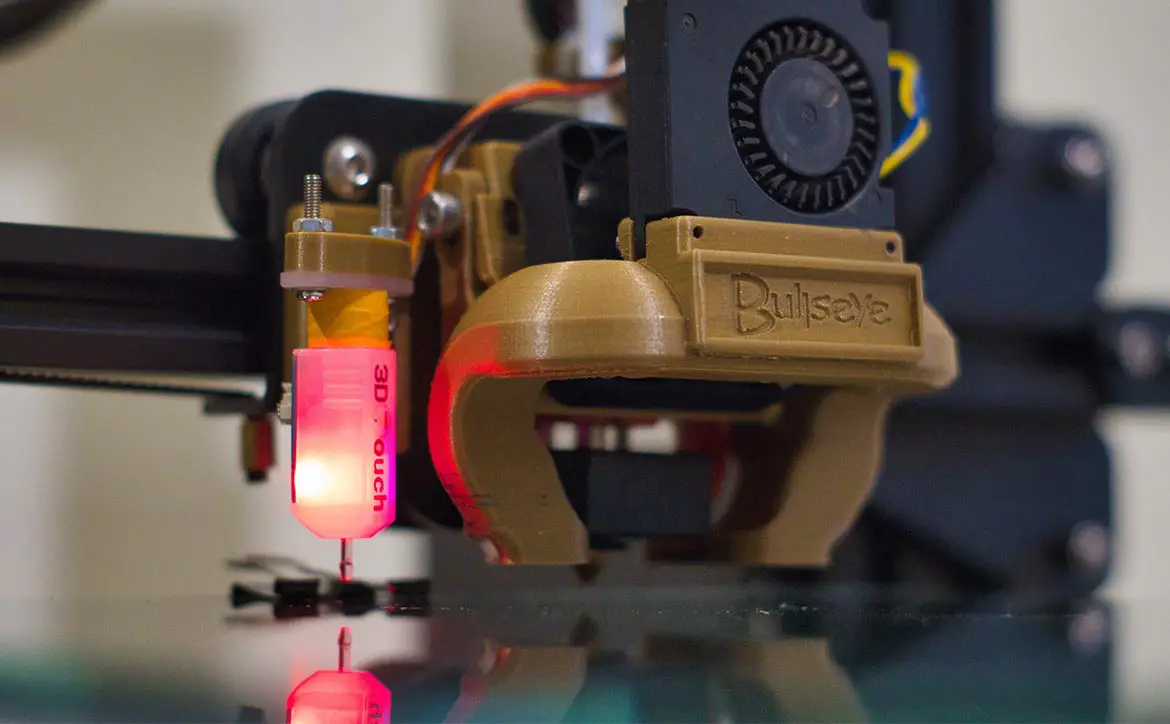
Additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, more commonly known as 3D printing, has the potential to be the next truly disruptive technology trend on a global scale. Additive manufacturing systems grow items one layer at a time from a blueprint using a feedstock material (typically a metal powder or polymer resin). The feedstock can either be sprayed from print heads or selectively melted by a laser or electron beam to seamlessly craft the object.
This growing versatility is crucial to the technology’s potential for revolutionizing supply chains. According to the 2019 Annual State of Logistics report, transportation costs businesses 10.4% of their revenue. That’s $1.04 trillion nationally. Imagine a future in which feedstock could be kept on hand by retailers in order to create products as demand arose. Inventory backlogs and shipping delays could rapidly become a thing of the past.
Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning boost additive manufacturing by increasing the sophistication of computer-aided drafting (CAD) programs. The CAD renders the design for the object to be built in three dimensions, one ultrathin slice at a time. The more precise the rendering, the better the print quality. This is yet another powerful example of analog and digital technologies aiding each other through convergence.
Green energy and sustainable design
Sustainability used to be just a trendy buzzword. Now it’s an imperative. According to Pew Research, about 65% of Americans think that the federal government is doing too little to address climate change. This is starting to change, with local, state, and national incentives spurring the development of green industry, especially in solar energy, which has already exceeded government efficiency targets. Unfortunately, politics, hamstrung by ideological agendas on all ends of the political spectrum, often have a less than a stellar track record of success. Thus, a more science-driven and DIY trend is emerging: sustainable design.
Two main philosophies exemplify this approach. Biophilia is the incorporation of nature into human spaces; the use of particular flora like English Ivy to remove toxins from the air is a prime example. On the other hand, biomimetic design aims to directly emulate natural processes, such as using gecko feet as an inspiration to create stronger adhesives.
The most ambitious designers are seeking to go far beyond the goal of sustainability to a regenerative design process that actively engages people in making the natural world objectively healthier because of our presence. The most stringent green building standard in the world, called the Living Building Challenge, has as its tagline “What if every single act of design and construction made the world a better place?” Carbon-negative industry and permaculture are both tools and endgame for this trending vision. Look for more buildings to be created using these design principles as a guide as the call for ecological responsibility becomes a groundswell in this lastest technology trend.
Aerospace development
Human spaceflight is a shockingly underrated technology, especially given its transformative potential. The issue is that it’s difficult for the average person to see the relevance of rocket ships and spinning planets to everyday life here on Earth. This lack of awareness constitutes a serious blind spot in our postmodern society, especially when so many tangible benefits are close to being realized.
In many ways, spaceflight has already paid dividends for global progress. A vast number of NASA spinoff technologies are already making an impact in the market. In fact, NASA has officially termed this its Technology Transfer Program, with 1920 products making the list as of 2016. Look for this to increase in the near future as NASA’s goals become more evident and partnerships with both global governments and private enterprise fuel development within the myriad industries that support space-based endeavors.
The true potential of human spaceflight has yet to be realized. We live in a world of finite resources; surrounding us, however, is a universe filled with more than enough riches to satisfy our civilization beyond the foreseeable future. Just one asteroid, called 511 Davida, is worth an estimated $26.99 quintillion dollars, and asteroid mining companies are already beginning to form. The inspirational successes of commercial spaceflight companies SpaceX, Virgin Galactic and Paragon SDC are providing a taste of what that prosperous future can be when human beings have the courage to embrace it.
The next decade is sure to bring technological advancements that we could scarcely have imagined at the turn of the millennium. Whether you’re a futurist or a traditionalist, keeping an eye on these emerging inventions will help you be a more informed citizen of the world.
What do you think about the emerging technology trends listed above? Which ones catch your eye the most? Let us know on social media by using the buttons below.
Last Updated on October 13, 2021.